Science News
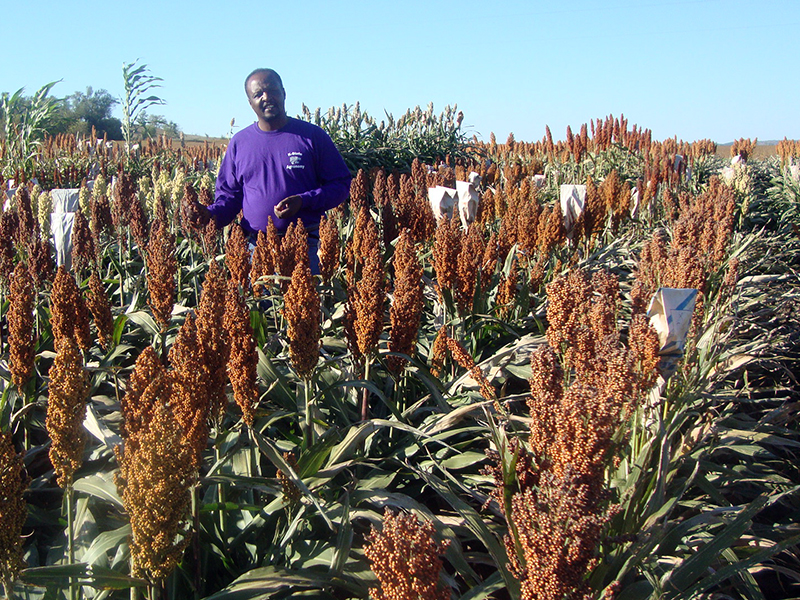

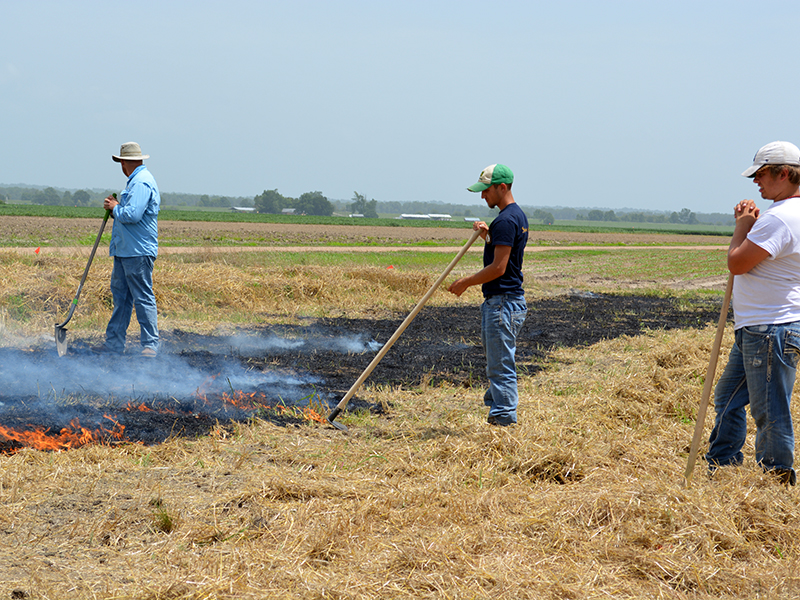
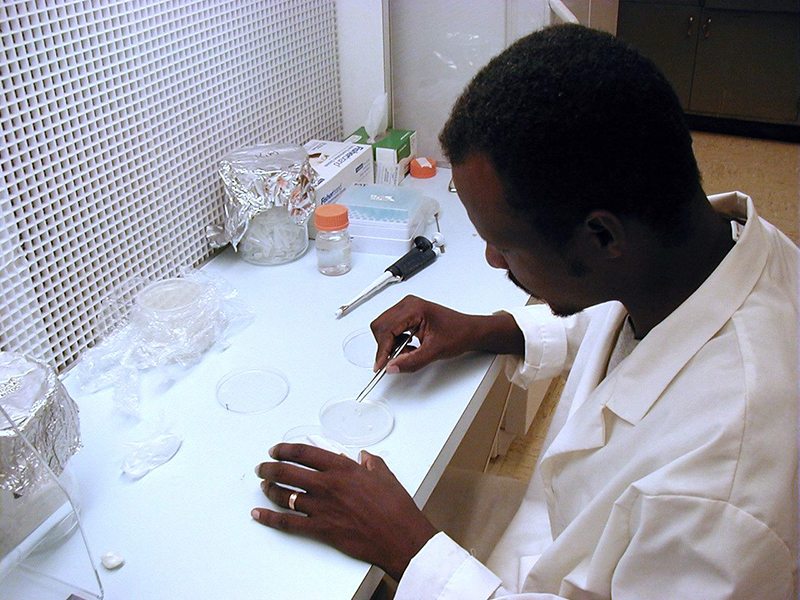
Sorghum, a common food item in regions of Africa and Asia, has one missing puzzle piece. The missing piece? Protein digestibility, which researchers in the Department of Agronomy at Kansas State University are trying to find.
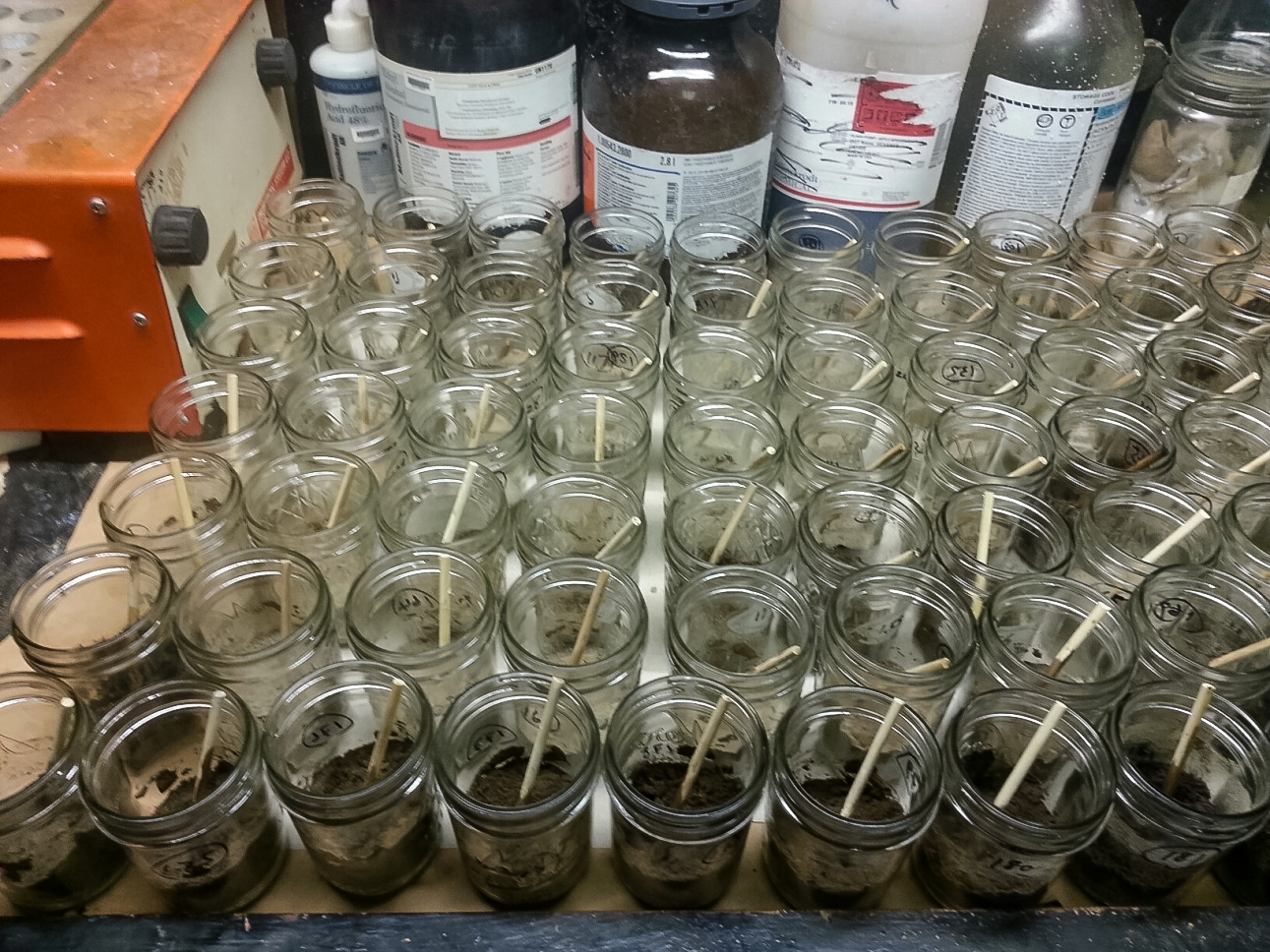

After an oil spill or leak, it’s important to act fast. If the oil has gotten into soil, scientists need to rapidly assess how much oil there is and how far it spread. It’s a process that has always been costly and time-consuming.
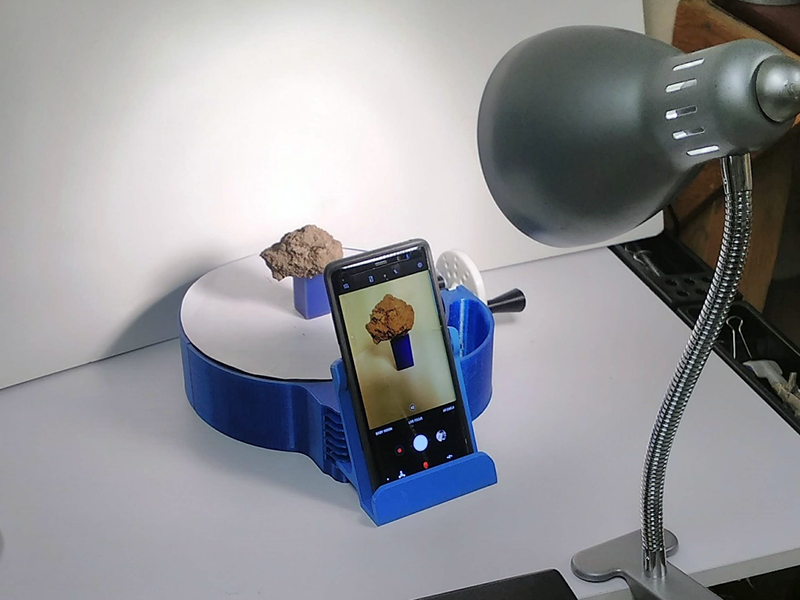


Seemingly everyone has a smartphone in their pocket, and we find new uses for them every day. They can help us avoid traffic jams or connect us to family from afar. They can even translate languages on the fly.
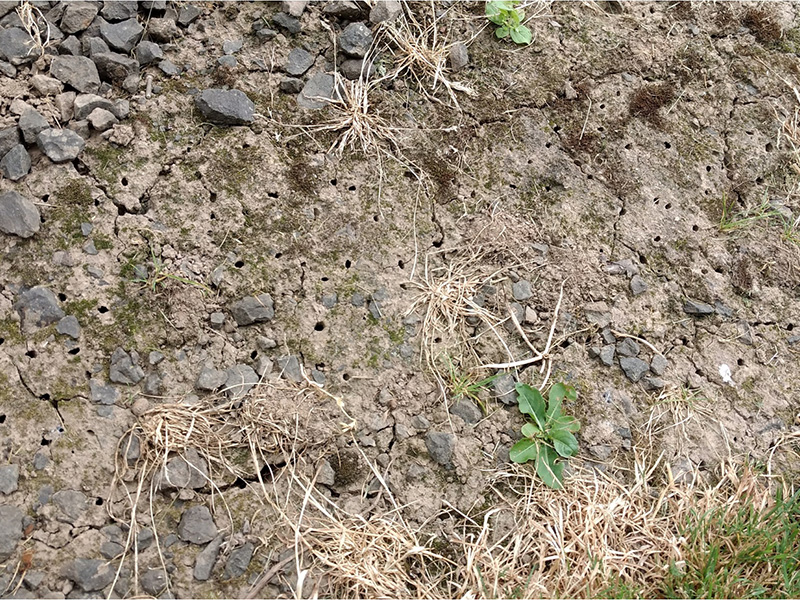


Many living creatures live in soil. Though their sizes range from microscopic soil microbes to larger animals like gopher turtles, they all call soil their “home.” Included in these ground-dwelling species are bees – vital in the pollination cycle of about 90% of plant life.
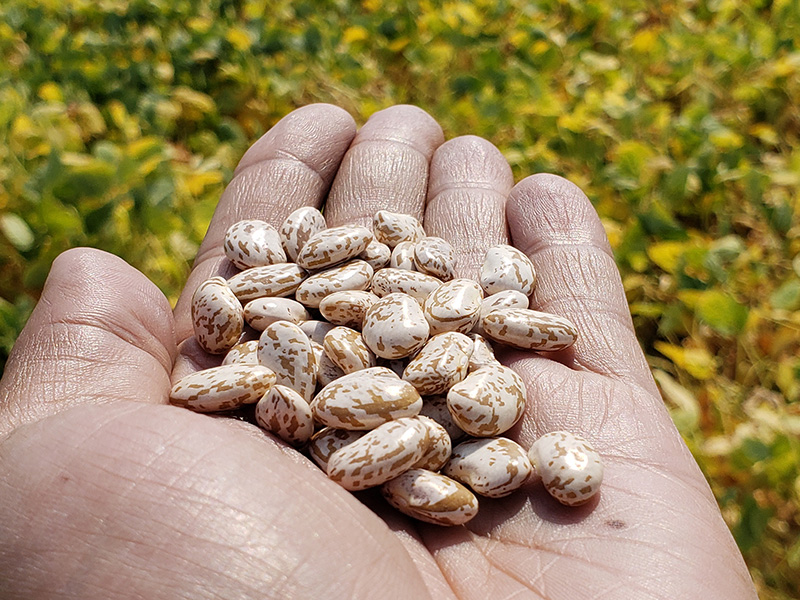


Pinto beans are good for us. They are nutritious, packed with protein and fiber. They also contain a host of micronutrients like B vitamins and folate.

But being good isn’t enough for pinto beans. They also need to look good.

For most of us, our closest encounter with the element fluorine is likely to be our toothpaste or a municipal water supply with added fluoride.

But excess fluorine can be a problem. For example, high levels of fluorine in the soil can hurt plants. Fluorine in soils may also affect microbes and other organisms higher along the food chain.

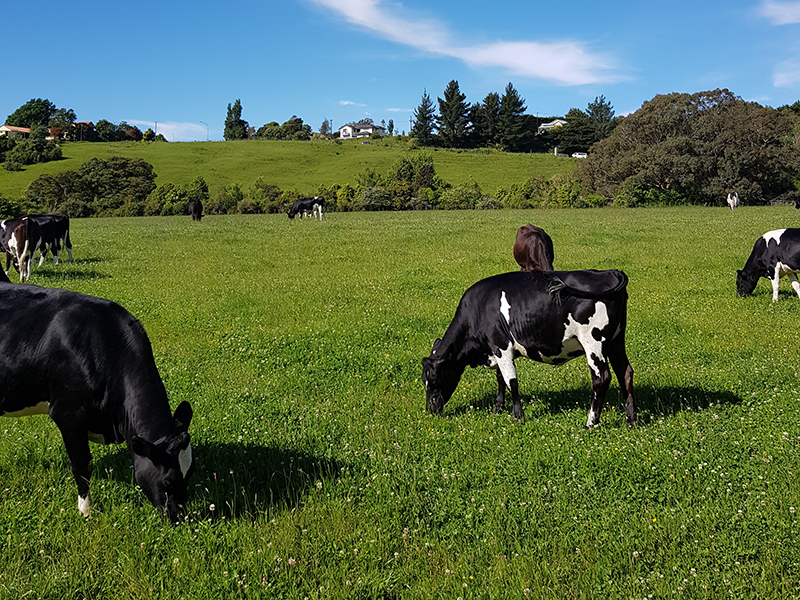
When it comes to soils, proper identification is key. Identification allows scientists to determine the story behind the soil: how it formed, how it behaves in different scenarios, and how valuable it may be to certain plants and animals.

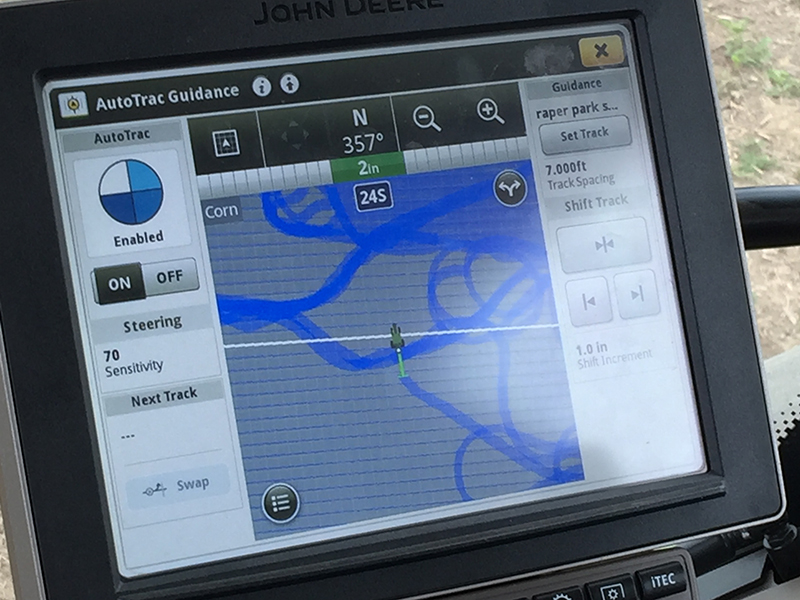
When it comes to nifty farm gadgets and technology, there are many neat tools. Tractor guidance is definitely one of them, thanks to how it helps farmers better use their resources.
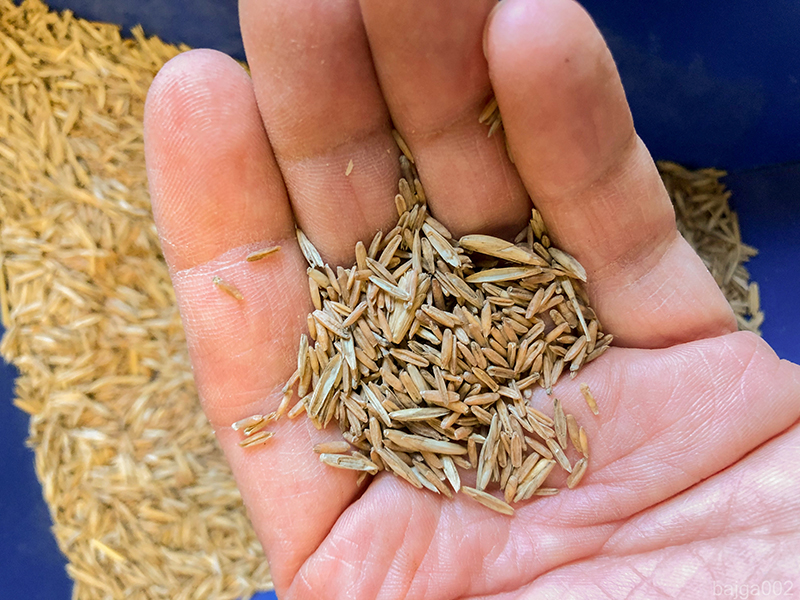


Wheatgrass is packed with beneficial nutrients, which makes the crop a popular superfood. And now, more farmers will have access to growing this beneficial crop.
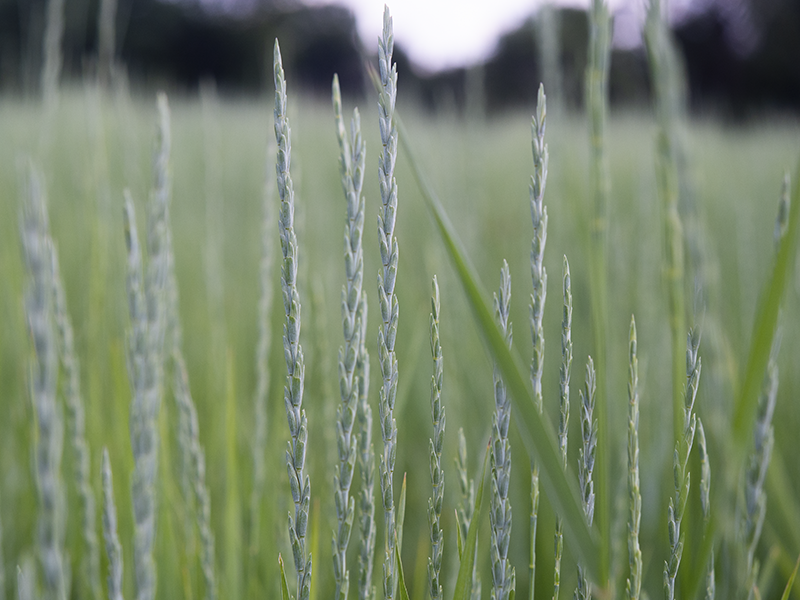

Historically, wheatgrass has been used as a crop in animal feed. However, a partnership between The Land Institute and the University of Minnesota changed that.

