Science News

Baking a cake from scratch has more variables than baking one from a boxed mix. Though one can debate why – and when – cake mixes were developed, they are popular, and produce a uniform product. (They were really patented in the 1930s!)
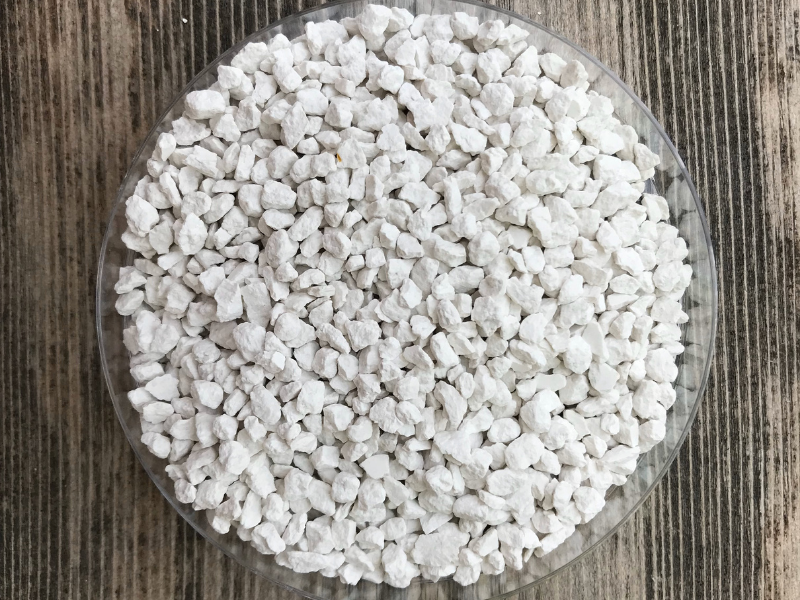

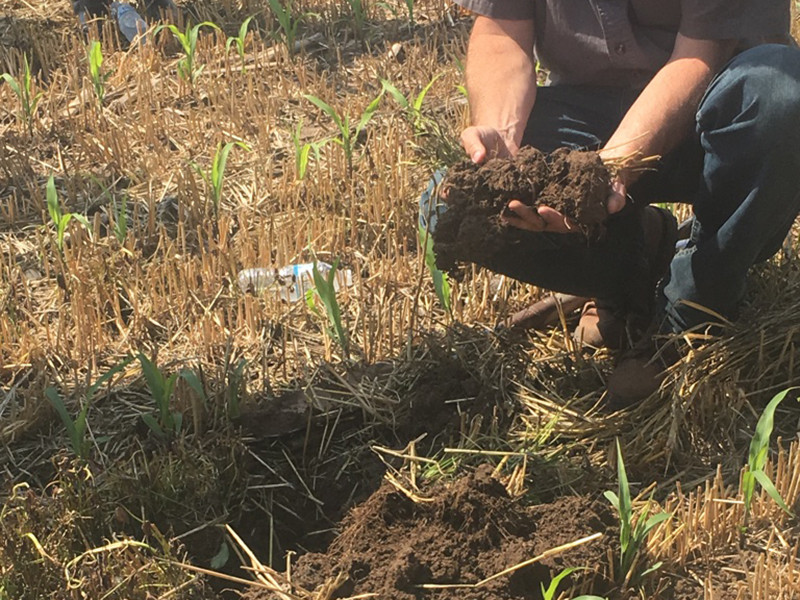
Studying new fertilizer options is the first step to getting farmers to eventually use them on their crops. A mineral called struvite has the potential to be an effective phosphorus fertilizer that may be considered organic.
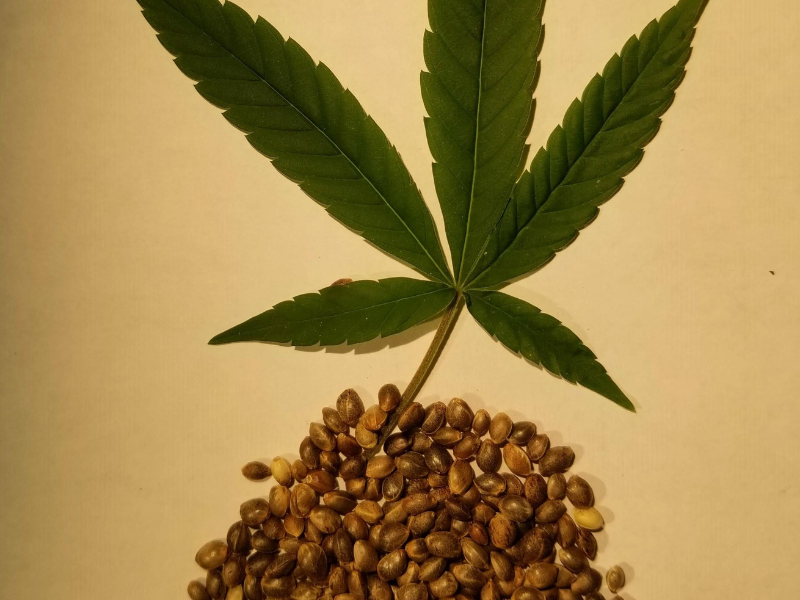

After decades of being relegated and regulated, research on industrial hemp as a valuable crop is far behind. That’s because the United States banned the use of hemp in the 1930s. The result was all research about this crop stopped, too. Now that the Farm Bill allows for the growing and use of industrial hemp, researchers have a decades-long gap in knowledge.
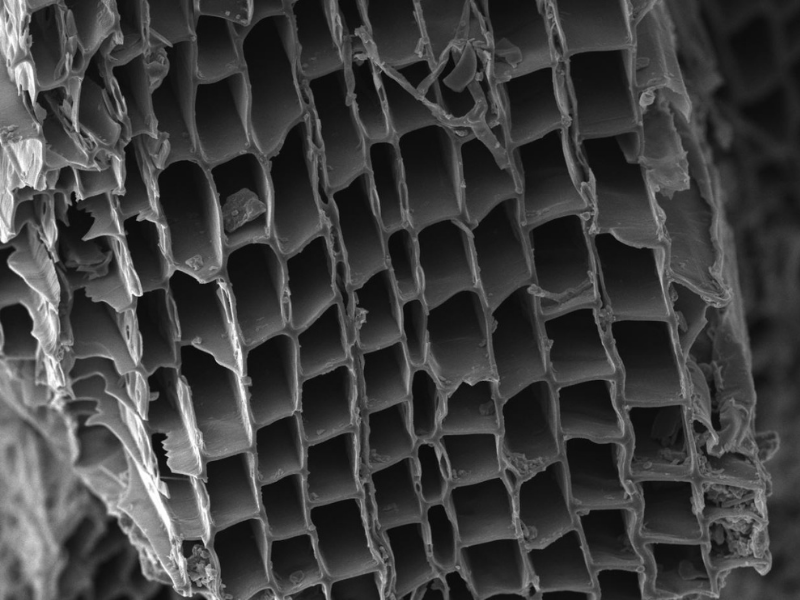
Biochar is similar to charcoal and can be added to soil with the goal of improving its quality. It can help increase nutrient and water retention. However, what happens in soil impacts fungi and plants that live there, and it is not always clear how they will react to biochar.
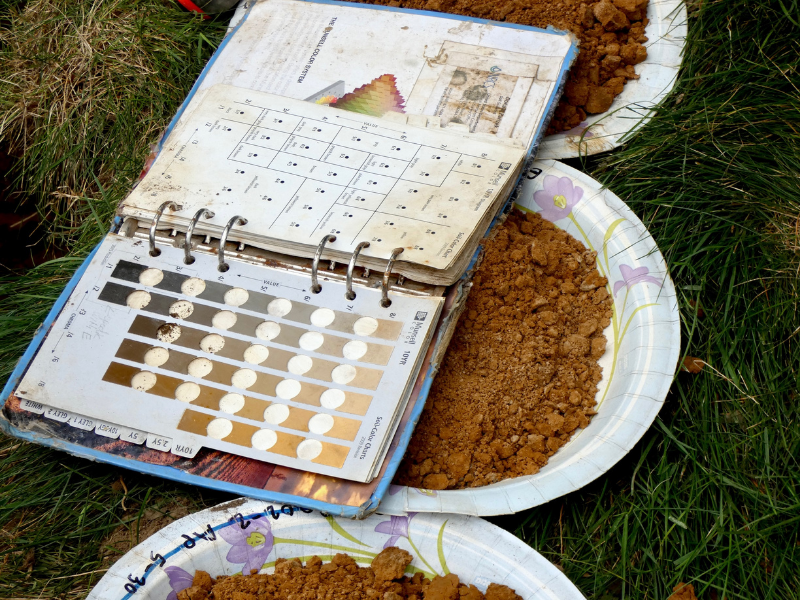

More than half the world’s population lives in urban areas. In the United States, more than 8 out of every 10 people are urbanites. Urban ecosystems often have less diverse animal and plant life compared to natural areas. But that’s not necessarily the case when it comes to microbes.

The world is warming. And fast. By 2050, it’s likely the planet will have warmed by about 3.6 degrees Fahrenheit compared to before the Industrial Revolution. That warming brings substantial changes. Storms will be stronger. People will run their air conditioners more. It will even change when and where our crops grow — and how well they perform.

Planting beneficial plants next to gardens and crop fields large and small has been a standard practice for decades, even centuries. The plants provide what are known as ecosystem services. These include attracting pollinators and preventing weeds.

A new study suggests we may have more opportunities to protect our waterways. That’s because one system for keeping too many nutrients out of streams could be used more widely than it is now.
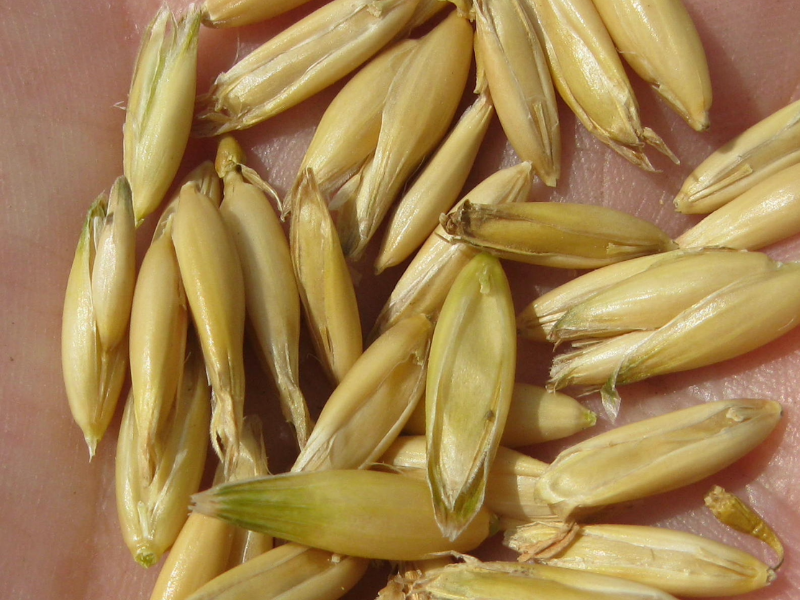


Oats are full of essential nutrients and are a great source of energy. They also provide dietary fiber, a key part of healthy, balanced diets.


The current modern economy creates a lot of waste. Waste that piles up in landfills, in water bodies and in city streets. In countries that can afford wastewater systems, human excreta are usually dealt with in a sanitary fashion. But for poorer countries, the disposal of human waste, especially in cities, can cause health problems.
